Generate a static website from python flask application using Frozen-Flask
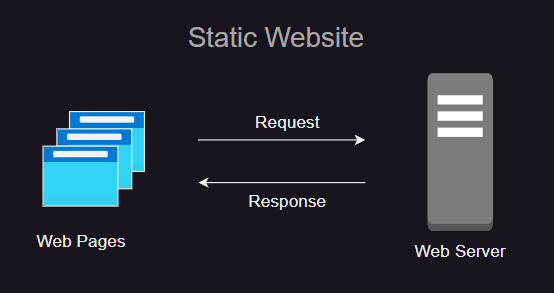
What is a static website
- A static website will deliver the content as is to the client with out any server-side rendering
- For example, a static website can just serve HTML, JavaScript and CSS files
Where can static websites be used
- Static websites can be used for websites where user inputs are not required. For example, an organization’s website, resume website, portfolio websites etc
Why use a static website
- Static websites are more secure with reduced attack surface since there is no scope for user input
- Static websites are easy to maintain and do not require more software to be installed on the server
- Static websites do not require databases
- Static websites can be easily hosted in robust, secure and performant web servers like IIS, apache2, nginx etc
What is frozen flask
- Frozen flask python module can be used to convert a python flask application into files which can be hosted as static website
- Hence python is also not required to host website
Why use frozen flask
- jinja templates in flask applications can facilitate re-usability in webpages. For example, a base HTML file with header, footer, menu etc., can be used in all website pages using jinja template
extendsandblockas shown below. This can help in organizing the website content easily
{% extends "base.html" %}
{% block title %}Contact{% endblock %}
{% block body %}
<div class="jumbotron">
<h1>The Contact Page</h1>
<p class="lead">Feel free to leave us a message at <a href="abc@xyz.com">abc@xyz.com</a></p>
</div>
{% endblock %}
- flask applications use routes, url_generators, blueprints for segregation and maintenance of webpages
Install frozen flask
- Run the following command to install the frozen-flask python module
python -m pip install Frozen-Flask
Sample flask application
- Below is a simple python flask application in a variable named
app
# app/__init__.py
from flask import Flask, render_template
# Initialize the app
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/')
def index():
return render_template("index.html")
@app.route('/about/')
def about():
return render_template("about.html")
@app.route('/contact/')
def contact():
return render_template("contact.html")
@app.route('/terms/')
def terms():
return render_template("terms.html")
- The server (variable named
app) can can be run with python for testing as shown below
# run.py
from app import app
import os
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(host="localhost", port=50100, debug=True)
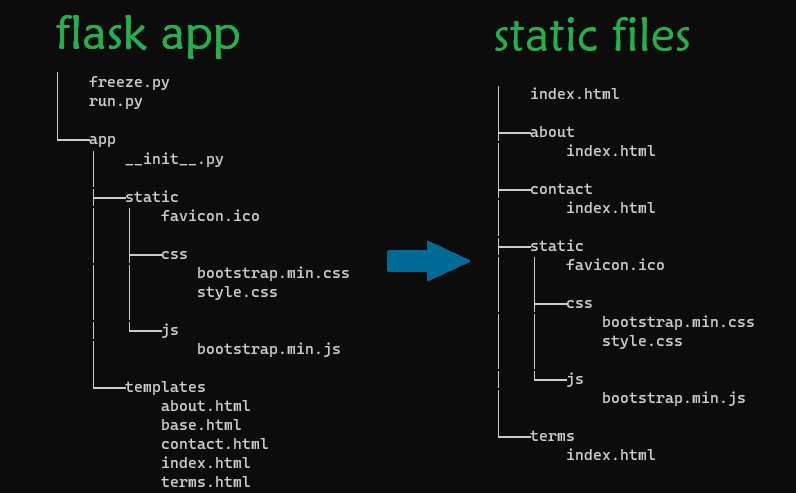
- The server can be converted into files using frozen-flask python module as shown below. The files will be generated into a folder named
buildnext tostaticandtemplatesfolders. Thesebuildfolder files can be hosted as a static website
# freeze.py
from flask_frozen import Freezer
from app import app
freezer = Freezer(app)
if __name__ == '__main__':
freezer.freeze()
Declaring routes in the flask server
- Make sure to declare the routes with
/at the end so that index.html file will be statically generated in the respective routes folder - For example, declare a route as
/about/so that the static file be generated in the path/about/index.html - Otherwise each route should be named with
.htmlat the end. For example, the flask route should be defined as/about.htmlinstead of/about
Video
Video for this post can be found here
References
- frozen-flask docs - https://frozen-flask.readthedocs.io/en/latest/
Comments
Post a Comment