Elasticsearch database introduction and terminology
- Elasticsearch is a distributed database where data is stored as JSON documents
- Elasticsearch is horizontally scalable, i.e., the database can run in multiple servers (nodes)
- Elasticsearch supports many data types like text, number, Geo-spatial, IP addresses etc
- Elasticsearch stores data in a data structure called inverted index, where data is literally stored as searches. This makes querying very fast even if vast amounts of data storage
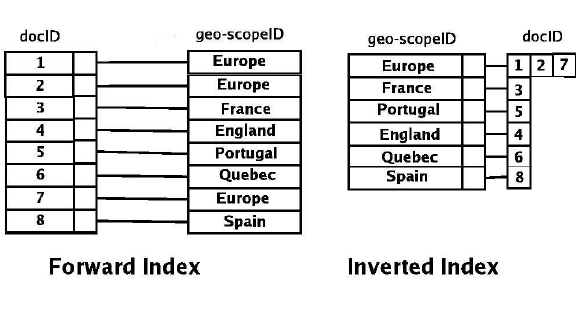

Analogy to Relational database
- Index is a collection of documents. It is like an RDBMS table.
| RDBMS | Elasticsearch |
|---|---|
| Table | Index |
| Row | JSON Document |
| Columns in a row | attributes of JSON document |

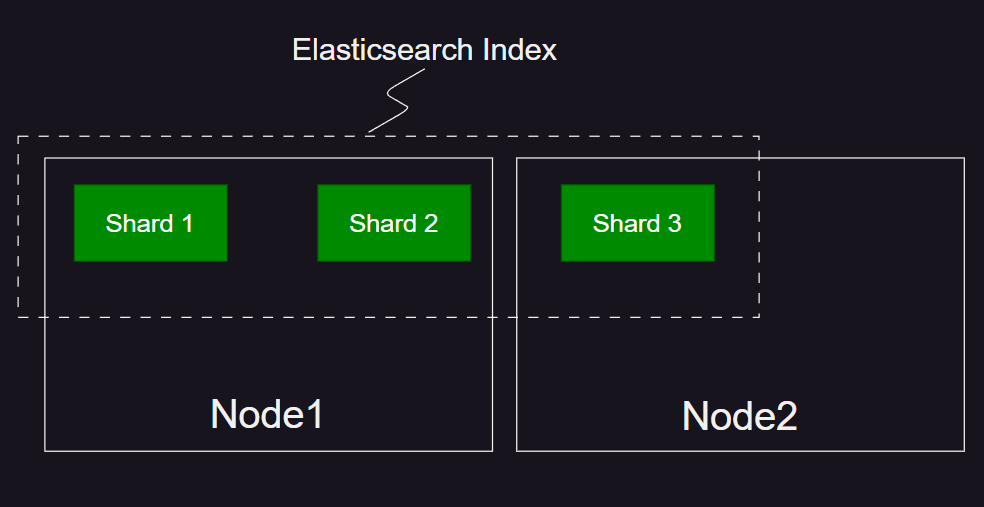
Nodes, Indexes and Shards
- Node means a computer (server) running Elasticsearch
- An Index is a logical group of one or more physical shards. Each shard is a Lucene index (a self-contained index)

- There are two types of shards: primary and replicas. Replica shards are for redundancy and serving data queries.
- The shards, data and queries are distributed among nodes to facilitate availability and scalability in a multi-node (multiple servers) cluster. The shards and data are automatically re-balanced when a node is added or removed
Index Template
- Index template is the settings applied to the index while creation. It is like a blueprint for creating an index
- Index template contains settings like number of shards and replicas, data mapping, priority etc.
- Index data mapping of an index template defines the schema of documents stored in the index. Index data mapping can be set to dynamic, so that the schema will be derived while the data is being ingested. This is also called Schema on Write. If the index data mapping is set to strict, just like an RDBMS, the index will reject the incoming documents not complying to the index data mapping properties.
- The following is an example console command to create an Index template
PUT _index_template/template_1
{
"index_patterns": ["te*", "bar*"],
"template": {
"settings": {
"number_of_shards": 1
},
"mappings": {
"_source": {
"enabled": true
},
"properties": {
"host_name": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"created_at": {
"type": "date",
"format": "EEE MMM dd HH:mm:ss Z yyyy"
}
}
},
"aliases": {
"mydata": { }
}
},
"priority": 500,
"composed_of": ["component_template1", "runtime_component_template"],
"version": 3,
"_meta": {
"description": "my custom"
}
}
Index alias in Elasticsearch

- An index alias is a group of indices. Documents can be inserted into an index group using alias. Only the index marked as write index can accept documents for insertion
- An alias can be specified to include all the indices following an index pattern (like mylogs-*). The following command creates an alias named “logs” that groups all indices starting with “logs-”
POST _aliases
{
"actions": [
{
"add": {
"index": "logs-*",
"alias": "logs"
}
}
]
}
- Using index alias with index lifecycle management, data of an index can be automated to roll over into new index based on a threshold age or size, so that the data of an index can be split into multiple indices for efficiency and tiered storage. Also splitting data into multiple indices also can utilize multi node cluster resources for parallel data queries
Data streams in Elasticsearch
- Data stream is an abstraction on top of index designed for append only time-series documents. The clients interact with data stream for updating documents. The data stream stores data in backing indexes (also called hidden indices).
- New index will be created as per the configured index lifecycle policy thresholds (like threshold age, threshold size etc.). Data can be queried from all indices but can be written only to the latest index.

Video
Video for this post can be found here
References
- What is Elasticsearch - https://www.elastic.co/what-is/elasticsearch
- Mapping database concepts with elastic search - https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/_mapping_concepts_across_sql_and_elasticsearch.html
- https://aravind.dev/everything-index-elastic/
- Elasticsearch from the bottom up - https://youtu.be/PpX7J-G2PEo
- Elasticsearch Index templates - https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/index-templates.html
- Elasticsearch alias - https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/aliases.html
- Elasticsearch datastreams - https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/data-streams.html
- Scalability and resilience - https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/scalability.html#:~:text=Each document in an index,searching or retrieving a document.
Comments
Post a Comment