Run python in browser with pyscript
Topics Covered
- What is pyscript
- What is WebAssembly
- Simple example with display and print python commands
- How pyscript works
- Use cases
- Configure python environment with external python packages, files, python scripts
- Access JavaScript from python
- Access python from JavaScript
- Create event handlers in python
- fetch external python scripts
- Manipulate DOM from python
What is pyscript
- pyscript is a framework to run python in browser
- pyscript uses a python interpreter compiled to Webassembly in the browser to run python scripts
- pyscript can also be configured to load external python packages, python scripts, files, plugins in the python environment
- JavaScript Code and python code can communicate with each other using pyscript

What is WebAssembly (WASM)
- WebAssembly is a low-level language like assembly language. It can be converted to a binary
.wasmformat that browsers can run. - Browser engines run WASM instructions through a WASM runtime
- WebAssembly instructions can run with near-native performance in the browser
- Other languages like C++, Rust, C#, Python can be compiled to WebAssembly and run in the browser
- The WASM modules and JavaScript modules can communicate with each other

Simple example
- Include the pyscript js and css files in HTML
- use
py-scripttag to write python code - The
printfunction writes output to browser console - The
displayfunction can display data in the web page. Read the docs about display function here - https://docs.pyscript.net/2023.09.1.RC2/user-guide/#pyscriptdisplay
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<!-- PyScript CSS -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://pyscript.net/snapshots/2023.09.1.RC2/core.css">
<!-- This script tag bootstraps PyScript -->
<script type="module" src="https://pyscript.net/snapshots/2023.09.1.RC2/core.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<py-script>
import datetime as dt
import sys
from pyscript import display
print("Hello from python!!!")
display(f"The time now is {dt.datetime.strftime(dt.datetime.now(), '%d %b %Y %H:%M')}")
display("Python details...")
display(sys.version)
</py-script>
</body>
</html>

How pyscript works
- pyscript JavaScript module is loaded in the browser
- python interpreter is setup in the browser based on the specified configuration files or
<py-config>tags - After the python environment is setup, the python code is discovered and run by pyscript
Use cases
- No need to install python, just include pyscript js module in a html file and run python in it
- UI for running python scripts can be created very easily
- Python based interactive applications can be easily created and shared
- Each browser window is an isolated python environment
- The python script runs in a browser sandbox which has limited access to OS files
Install external python packages
- Use py-config tags in the HTML page to install external python packages from pip like the following
<py-config>
packages = ["matplotlib", "pandas"]
</py-config>
- Version of python package can also be specified (like
"pandas==2.1.2") - The config information also be kept in a file (say
pyConfig.toml) and linked in HTML like the following. But this approach, the files should be hosted and served as static files from a server
<py-script config="pyscript.toml">
<!--python code goes here-->
</pyscript>
- The example below uses
matplotlibpython package from pip and displays the output in a specific div - The
displayfunction can also display images to a div as shown in this example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://pyscript.net/snapshots/2023.09.1.RC2/core.css">
<script type="module" src="https://pyscript.net/snapshots/2023.09.1.RC2/core.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<py-config>
packages=["matplotlib"]
</py-config>
<div>
<div id="output"></div>
<py-script>
from pyscript import display
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = [1, 2, 3, 4]
y = [1, 4, 2, 3]
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
la, = ax.plot(x, y)
ax.set_title('Basic Matplotlib plot')
ax.set_xlabel("X Data")
ax.set_ylabel("Y Data")
la.set_label('basic_plot')
ax.legend()
# display the plot
display(fig, target="output")
</py-script>
</div>
</body>
</html>

Call JavaScript from python
- In the below example, the python script is calling a JavaScript function named
createTableand is also passing data to the function. Using thejspython module, the python script can access the JavaScript functions of the web page - strings and numbers can be directly passed to JavaScript functions. But objects, lists, functions are passed to JavaScript as Proxy objects. Hence in this example as a workaround we have created a JSON string from dictionary and parsed it in the JavaScript
- The
documentandwindowvariables imported from pyscript can be used to access thedocumentandwindowvariables from JavaScript
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<!-- PyScript CSS -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://pyscript.net/snapshots/2023.09.1.RC2/core.css">
<script type="module" src="https://pyscript.net/snapshots/2023.09.1.RC2/core.js"></script>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://cdn.datatables.net/1.13.6/css/jquery.dataTables.min.css">
<script type="module" src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.7.0.js"></script>
<script type="module" src="https://cdn.datatables.net/1.13.6/js/jquery.dataTables.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
function createTable(tableData){
console.log(tableData)
new DataTable('#example', JSON.parse(tableData));
}
</script>
<div>
<table id="example" class="display" width="100%"></table>
<py-script>
import js
import json
from pyscript import window
dataSet = [
['Tiger Nixon', 'System Architect', 'Edinburgh', '5421', '2011/04/25', '$320,800'],
['Garrett Winters', 'Accountant', 'Tokyo', '8422', '2011/07/25', '$170,750'],
['Ashton Cox', 'Junior Technical Author', 'San Francisco', '1562', '2009/01/12', '$86,000'],
['Cedric Kelly', 'Senior Javascript Developer', 'Edinburgh', '6224', '2012/03/29', '$433,060'],
['Airi Satou', 'Accountant', 'Tokyo', '5407', '2008/11/28', '$162,700'],
['Unity Butler', 'Marketing Designer', 'San Francisco', '5384', '2009/12/09', '$85,675'],
]
tableData = {
"columns": [
{ "title": 'Name' },
{ "title": 'Position' },
{ "title": 'Office' },
{ "title": 'Extn.' },
{ "title": 'Start date' },
{ "title": 'Salary' }
],
"data": dataSet
}
js.createTable(json.dumps(tableData))
window.alert("data table loaded from python")
</py-script>
</div>
</body>
</html>

Call python from JavaScript
- There is no direct way to call python from JavaScript
- Hence a JavaScript function
createObjectis declared which will be called by python script to attach python objects and functions in JavaScript - Since we are passing a function object to JavaScript from python,
create_proxyis used - The python values or functions are attached to JavaScript only after the script is executed. JavaScript can detect the completion of python script execution using the py:all-done window event
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<!-- PyScript CSS -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://pyscript.net/snapshots/2023.09.1.RC2/core.css">
<!-- This script tag bootstraps PyScript -->
<script type="module" src="https://pyscript.net/snapshots/2023.09.1.RC2/core.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
function createObject(object, variableName) {
globalThis[variableName] = object
}
</script>
<div>
<py-script>
print("Hello from python!!!")
import js
from pyodide.ffi import create_proxy
def multiplier(n, m):
return n*m
js.createObject(create_proxy(multiplier), "multiplier_js")
name = "TamingPython"
js.createObject(name, "names_js")
</py-script>
</div>
<script>
window.addEventListener("py:all-done", function () {
console.log(globalThis.multiplier_js(5, 3))
console.log(globalThis.names_js)
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
Create event handlers in python
- Using the
py-clickHTML attribute, python event handlers can be declared in HTML - Also
@whendecorator can be used in python script to intercept the event of an element selected with query selector string - The event variable in the python event listener can be used just like in JavaScript (like
event.targetetc)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<!-- PyScript CSS -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://pyscript.net/snapshots/2023.09.1.RC2/core.css">
<!-- This script tag bootstraps PyScript -->
<script type="module" src="https://pyscript.net/snapshots/2023.09.1.RC2/core.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<py-config>
{
"packages": ["arrr"]
}
</py-config>
<div>
<h1>Polyglot 🦜 💬 🇬🇧 ➡️ 🏴☠️</h1>
<p>Translate English into Pirate speak...</p>
<input type="text" id="english" placeholder="Type English here..." />
<button py-click="translate_english">Translate</button>
<button id="test_btn">Test</button>
<div id="output"></div>
</div>
<py-script>
print("Hello from python!!!")
import arrr
from pyscript import document, when
def translate_english(event):
input_text = document.querySelector("#english")
english = input_text.value
output_div = document.querySelector("#output")
output_div.innerText = arrr.translate(english)
@when("click", "#test_btn")
def when_demo(event):
output_div = document.querySelector("#output")
output_div.innerText = "Button click event intercepted with 'when' and querySelector"
</py-script>
</body>
</html>

Link external python scripts
- For this approach, the the files should be hosted as static files from a server instead of directly opening the HTML file in the browser
main.pyandappConfig.tomlare declared in the script tagmain.pyuses theappUtils.pyfile. So the file needs to explicitly fetched through the configuration fileappConfig.toml
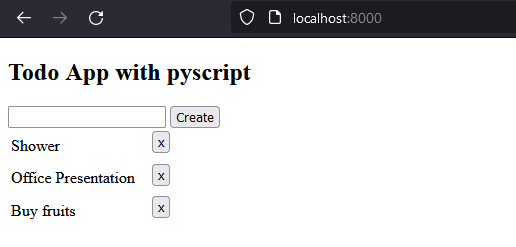
<!--index.html-->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://pyscript.net/snapshots/2023.09.1.RC2/core.css">
<script type="module" src="https://pyscript.net/snapshots/2023.09.1.RC2/core.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Simple Todo App with pyscript</h2>
<input type="text" id="todoInp"/>
<button id="createTodoBtn">Create</button>
<table id="todosTable"></table>
<script type="py" src="./main.py" config="appConfig.toml"></script>
</body>
</html>
# appConfig.toml
[[fetch]]
files = ['appUtils.py']
# main.py
from pyscript import document, window
from pyscript import when
from appUtils import createTodoElement
@when("click", "#createTodoBtn")
def click_handler(event):
print("Add todo button is clicked")
todoTxtInpEl = document.querySelector("#todoInp")
todoTxt = todoTxtInpEl.value.strip()
if todoTxt == "":
window.alert("Todo text is empty...")
return
todoRow = createTodoElement(todoTxt)
todosTable = document.querySelector("#todosTable")
todosTable.appendChild(todoRow)
todoTxtInpEl.value = ""
# appUtils.py
from pyscript import document
def createTodoElement(todoTxt:str):
deleteBtn = document.createElement("button")
label = document.createElement("label")
label.innerText = todoTxt
deleteBtn.innerText = "x"
deleteBtn.style.marginLeft = "1em"
deleteBtn.style.marginBottom = "0.5em"
deleteBtn.classList.add("btn")
deleteBtn.classList.add("btn-danger")
todoRowEl = document.createElement("tr")
todoLabelCell = document.createElement("td")
todoDelBtnCell = document.createElement("td")
todoLabelCell.appendChild(label)
todoDelBtnCell.appendChild(deleteBtn)
todoRowEl.appendChild(todoLabelCell)
todoRowEl.appendChild(todoDelBtnCell)
def del_task(evt):
print("Deleting task...")
rowEl = evt.target.parentNode.parentNode
tableEl = rowEl.parentNode
tableEl.removeChild(rowEl)
deleteBtn.onclick = del_task
return todoRowEl
Access and manipulate HTML from python
- In the above example,
document.querySelectoris used to reference HTML elements in python.event.targetis used in python event listener to reference the event originating element (the button) - functions or attributes like
appendChild,removeChild,value,parentNode,innerText,classList,styleare called in python on elements just like python
Video
You can the video on this post here
References
- pyscript site - https://pyscript.net/
- pyscript beginner guide - https://docs.pyscript.net/2023.09.1.RC2/beginning-pyscript/
- pyscript docs - https://docs.pyscript.net/2023.09.1.RC2/user-guide/
- pyscript demos - https://pyscript.net/examples/
Comments
Post a Comment