Overview of Web APIs and API security
What is an API?
- API (Application Programming Interface) is a way two applications can talk to each other
- API is a specification that defines the request and response formats, how to call the server etc.
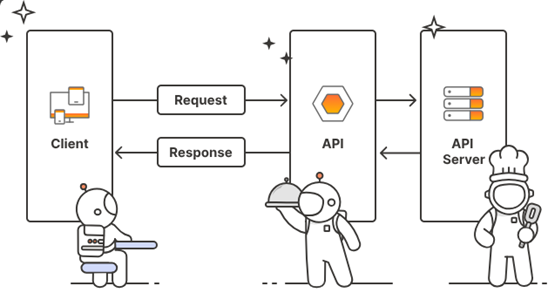
Why APIs
Modular systems
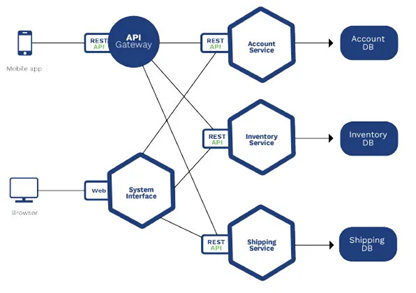
A system can be developed as modules by different teams instead of a Monolith and modules can communicate with well defined APIs
Information Hiding
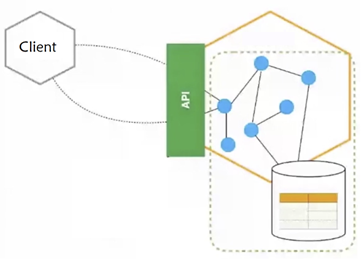
API Client/User need not know the internals.For example, an API server can be developed in Python or Java and client will not know
Extend applications
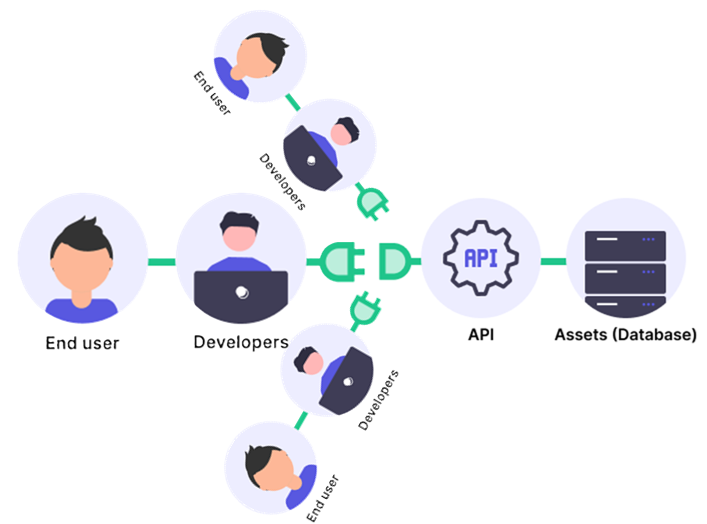
A main application can expose API to allow third party developers to create new applications
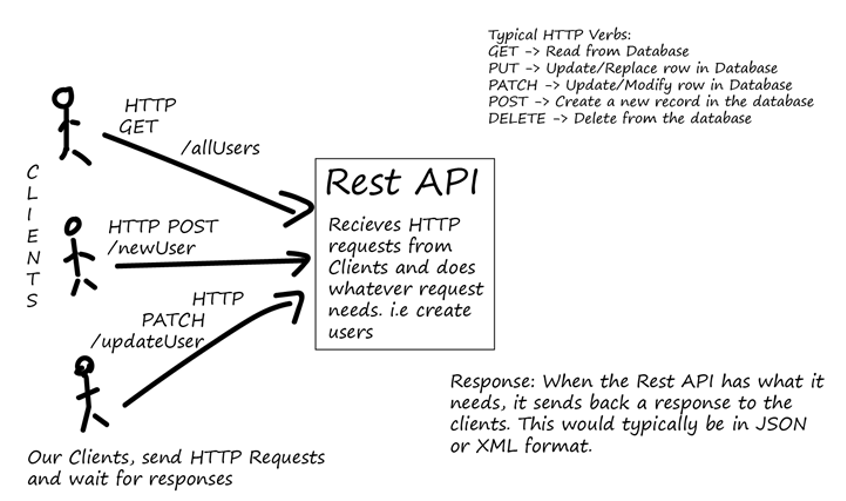
Web API Example
GET Request
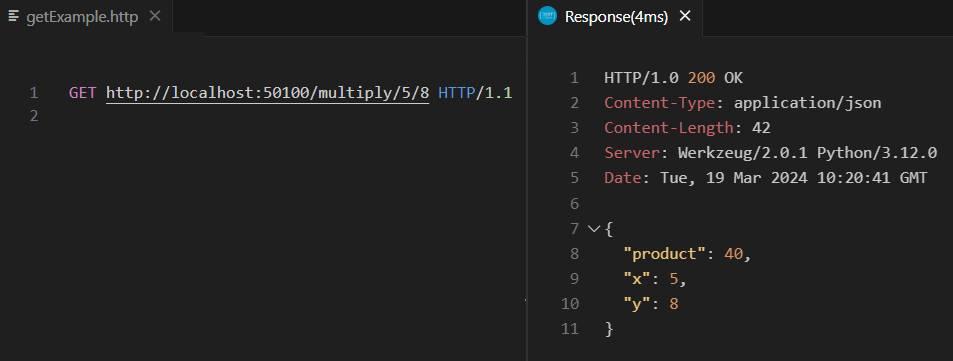
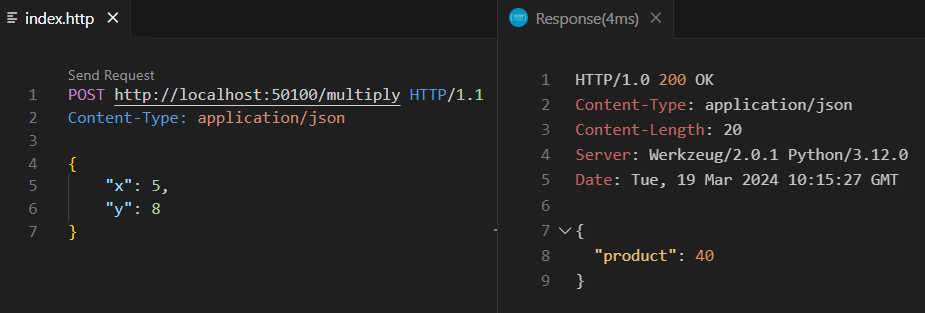
POST request
Web API
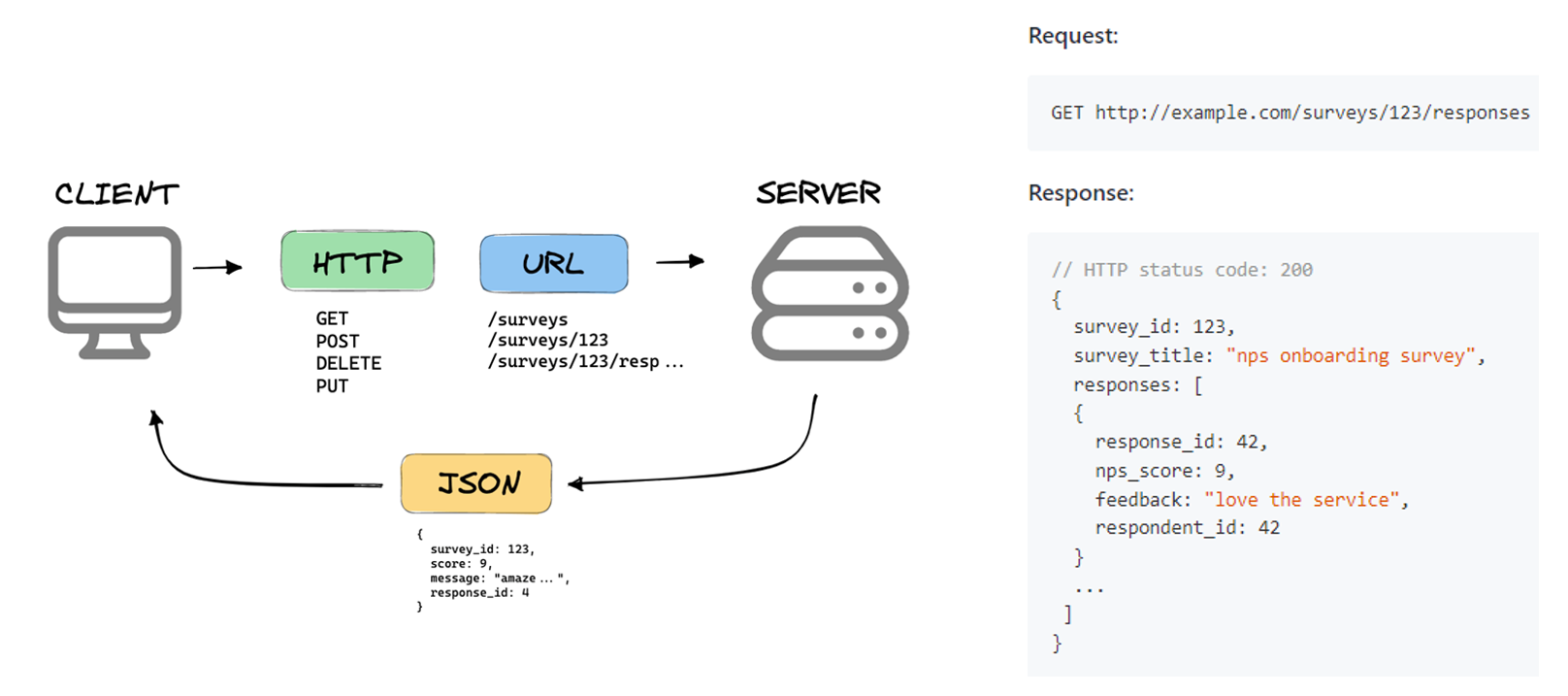
Web API is API to communicate with a server over the web/HTTP
HTTP Protocol
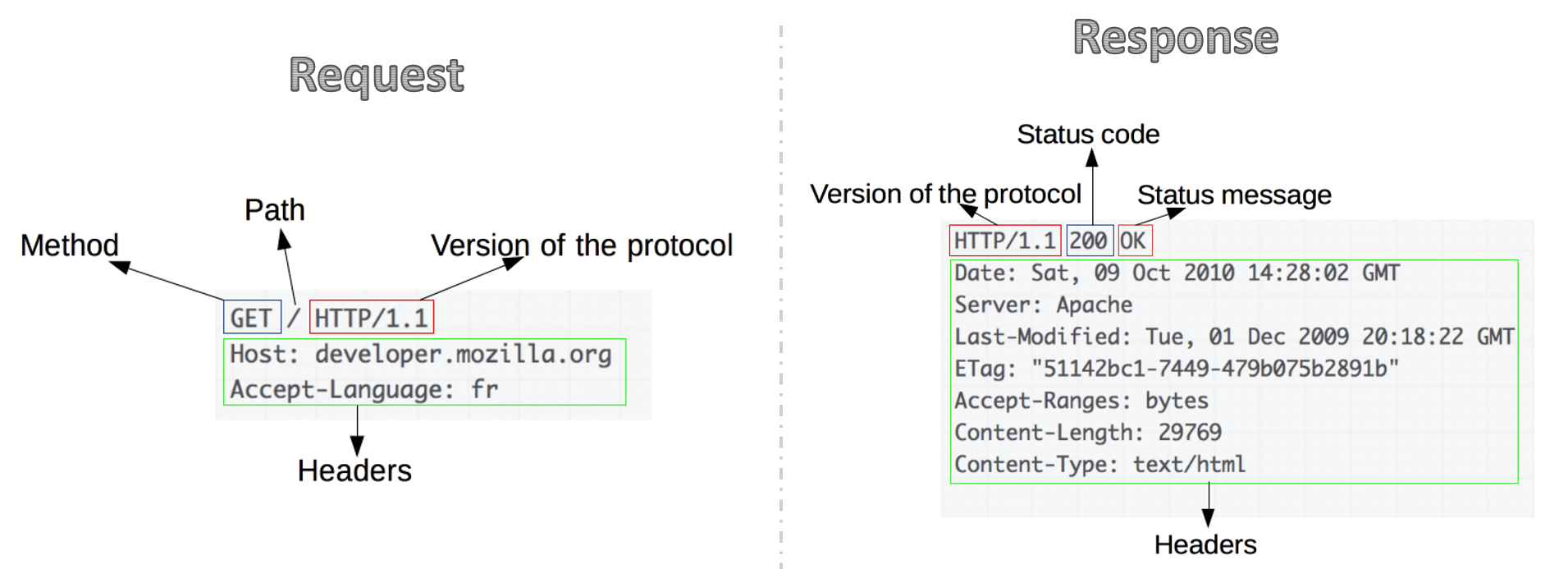
HTTP is the protocol used to transfer content over the web
REST API
REST API is an architectural style that allows clients to communicate with server resources with standard HTTP verbs like GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, HTTP status code for response status, URL parameters for querying etc.
How to call APIs
- Postman – Browser like tool to call web APIs
- REST Client – Visual Studio Code extension
- cURL – command line utility
- Libraries in programming languages – requests module in python, HttpClient class in dotnet, Java
Postman
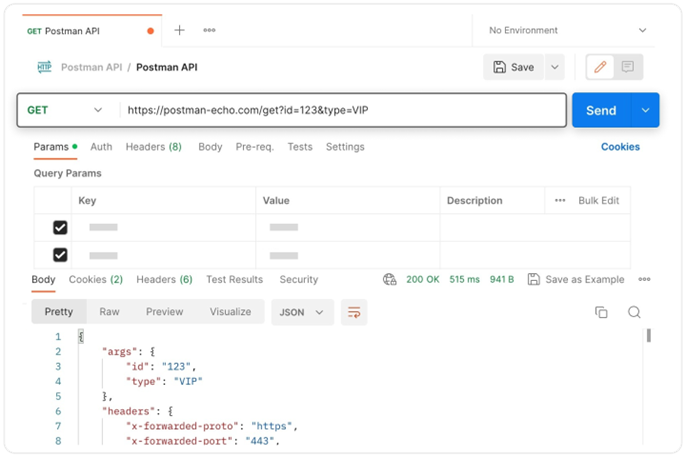
Postman is a popular to interact with APIs with a convenient UI just like a web browser
Visual Studio Code REST Client Extension

This Visual studio code extension can be used to interact with APIs conveniently in VS code
cURL command line utility
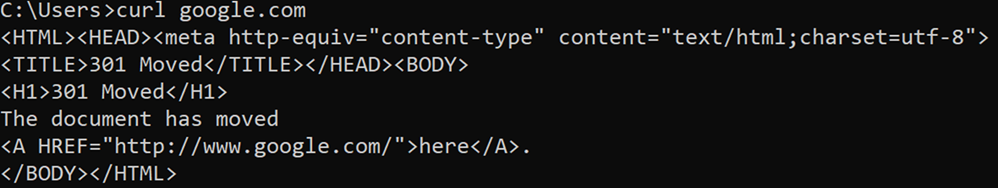
HTTP requests can be done from command line with the cURL command line utility
Libraries in programming languages
import requests
# POST request form data as a python dictionary
postData = {
'x': 5,
'y': 8
}
# Perform HTTP POST request along with post body and get response object in return
resp = requests.post(url='<http://localhost>: 50100/multiply', json=postData)
# check is response status_code is 200
if not resp.ok:
print("Some unexpected response received...")
# parse the response text as a JSON and get a python dictionary from the response
respData = resp.json()
print(respData)
print(f"The multipication result is {respData["product"]}")
- Libraries like requests module in python, HttpClient in dotnet, Java can be used to easily call APIs from applications
Hosting APIs
from flask import Flask, request
app = Flask(__name__)
# extract data from post request body
@app.route('/multiply', methods=['POST'])
def multiplyWithPostBody():
reqJson = request.get_json()
x = reqJson['x']
y = reqJson['y']
prodVal = x * y
return {"product": prodVal}
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=50100, debug=True)
- Create a program that listens for requests and creates responses as per the API specification
- A web server can be created to implement Web API server
- A simple python flask example can be seen above
HTTP status codes
- Server can set HTTP status codes along with the response body to convey the response outcome
- Some important and most used HTTP response status codes are
| 201 Created | 1xx: Informational |
| 204 No Content | 2xx: Success |
| 301 Moved Permanently | 3xx: Redirection |
| 400 Bad Request | 4xx: Client Error |
| 401 Unauthorized | 5xx: Server Error |
| 404 Not Found | |
| 403 Forbidden | |
| 409 Conflict | |
| 500 Internal Server Error |
API security measures
Whitelisting
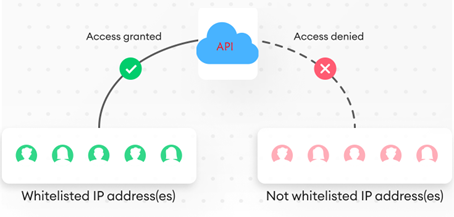
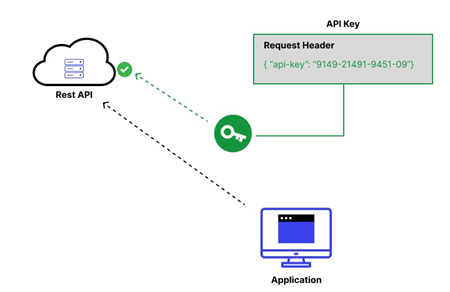
Credentials
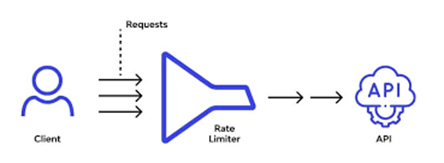
Rate Limiting
Secure Token Service (STS)
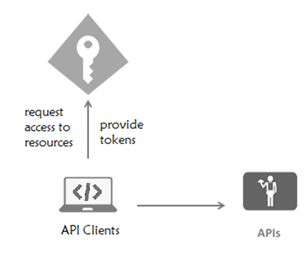
- API Clients and servers are registered in the STS
- Clients request short-lived tokens for API access
- API servers validate the tokens for authorization
Client Credentials API authorization flow

In Client Credentials OAuth 2.0 authorization flow, the client application sends its client ID and client secret to the STS, receiving an access token in response. Then the client application uses this access token to access data from the resource server.
Video
Video on this post can be seen here
Comments
Post a Comment